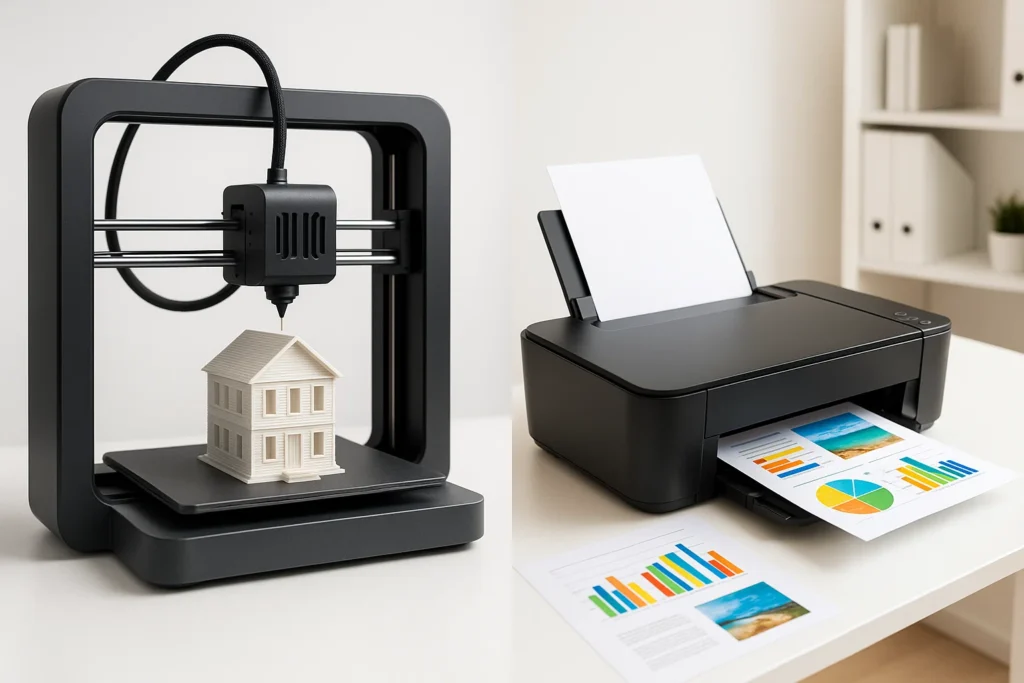
Printers have evolved dramatically over the years. What once started as simple inkjet and laser devices used for documents has now expanded into machines capable of building physical objects. Today, businesses and individuals are increasingly comparing 3D printers vs traditional printers to understand their unique roles and how they can work together.
Whether you are a student, designer, engineer, or small business owner, choosing between 3D and traditional printing technologies depends on your needs. While traditional printers are essential for text, photos, and paperwork, 3D printers open up new possibilities in manufacturing, prototyping, and creative design. The two are not necessarily competitors but rather complementary tools that enhance each other’s value.
Let’s dive deeper into the differences, advantages, and combined uses of these two technologies.
Understanding Traditional Printers
Traditional printers, such as inkjet and laser models, are designed to produce two-dimensional outputs on flat surfaces like paper, fabric, or labels. Their main purpose is to reproduce text, graphics, and images quickly and at an affordable cost.
Most households and offices rely on these machines daily. Whether it’s printing invoices, marketing flyers, or school assignments, traditional printers remain a core part of professional and personal life. They offer speed, affordability, and accessibility, which is why they remain so widely used.
What Are 3D Printers?
3D printers are an entirely different class of technology. Instead of printing ink or toner on paper, they create three-dimensional objects layer by layer using materials such as plastic, resin, or even metal.
The process, called additive manufacturing, allows users to design and build products that were once only possible through industrial-scale machinery. From medical implants and mechanical parts to toys and art sculptures, 3D printing opens up new opportunities across industries.
Unlike traditional printers, which are limited to 2D representation, 3D printers bring imagination into reality by producing fully functional objects.
Key Differences Between 3D Printers vs Traditional Printers
Printing Method
Traditional printers work by transferring ink or toner onto flat surfaces. In contrast, 3D printers build objects layer by layer, making them ideal for physical products rather than just documents.
Output Medium
Traditional printers use paper, labels, and fabric. 3D printers use filament, resin, or powder-based materials to create durable, solid structures.
Cost and Accessibility
Standard printers are generally inexpensive and widely available. However, 3D printers tend to be more costly, with expenses not only for the machine itself but also for raw materials and software.
Purpose and Application
Traditional printers excel at producing text, photos, and graphic materials quickly. 3D printers, on the other hand, focus on design, engineering, prototyping, and manufacturing, making them a valuable tool for innovators and creators.
How 3D Printers Complement Traditional Printers
Instead of replacing each other, both technologies can work side by side. For example, a design firm may use traditional printers for creating documentation, reports, or design drafts. At the same time, they may use 3D printers to produce models or prototypes of the projects they are working on.
This complementary relationship enhances creativity and efficiency. A business that integrates both can enjoy the best of both worlds quick documentation with traditional printing and innovative product design with 3D printing.
Industries Benefiting from Both Printing Technologies
Education
Schools and universities often use traditional printers for worksheets, exams, and course materials. Meanwhile, 3D printers allow students to engage in hands-on learning by creating prototypes, architectural models, or science projects.
Healthcare
Hospitals and clinics use traditional printers for patient records, prescriptions, and documentation. Simultaneously, 3D printers are used to create prosthetics, surgical models, and even bioprinted tissues.
Architecture and Design
Architects use traditional printers to print floor plans and project documents. At the same time, they can bring their ideas to life with 3D printers by creating physical scale models of buildings.
Manufacturing
Factories still use traditional printers for labeling, documentation, and safety instructions. However, 3D printers play a growing role in rapid prototyping and custom part production, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Choosing the Right Printer for Your Needs
If your main focus is printing documents, photos, or marketing materials, a traditional printer is still the most practical choice. But if you need to create models, product prototypes, or innovative designs, 3D printers offer unmatched versatility.
For small businesses or creative professionals, investing in both can bring long-term benefits. In fact, many companies now search for printers for sale that combine both traditional and 3D printing capabilities to expand their productivity.
The Future of Printing Technology
Both traditional and 3D printers continue to evolve. Traditional printers are becoming faster, more energy-efficient, and capable of higher-quality photo reproduction. On the other hand, 3D printers are advancing toward mass production, faster print speeds, and the ability to print with more materials, including sustainable and recyclable options.
The convergence of these technologies may eventually give us hybrid machines that can print both documents and physical objects. While we are not there yet, the future of printing looks promising.
Conclusion
When comparing 3D printers vs traditional printers, it is clear that both have their unique strengths and limitations. Traditional printers excel at efficiency, affordability, and producing 2D documents. 3D printers, however, unlock creativity by building physical models and prototypes that push innovation forward.
Rather than replacing one another, they complement each other beautifully. Businesses, educators, healthcare providers, and designers can benefit from using both technologies side by side.
As printing technology continues to evolve, the combination of 3D printers and traditional printers will shape industries, inspire creativity, and provide practical solutions in ways we could only imagine a few decades ago.