The Microbial Inoculants Market has become one of the most important components of modern agriculture as farmers and industries embrace sustainable methods that enhance soil health and boost crop productivity. Microbial inoculants, sometimes referred to as bioinoculants, are formulations that contain beneficial microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, or algae. These organisms improve nutrient availability, stimulate plant growth, and promote soil fertility through natural processes. As global demand for food continues to rise and environmental pressures intensify, microbial inoculants are increasingly viewed as essential agricultural inputs capable of reducing dependence on chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
Growing awareness of soil degradation and concerns related to climate change have further accelerated the adoption of microbial products. Farmers across the world are seeking solutions that enhance resilience against drought, pests, and nutrient depletion. Microbial inoculants offer a sustainable alternative that aligns with regenerative agriculture practices, making them valuable for both small-scale and large-scale farming operations.
Market Evolution
The development of microbial inoculants began with the introduction of early biofertilizers used primarily for nitrogen fixation in legume crops. Over time, scientific advancements expanded the range of microbial strains that could be used to support plant growth. Modern inoculants include phosphate-solubilizing bacteria, potassium-mobilizing microbes, and fungi that improve nutrient absorption. Research in plant-microbe interactions has helped identify strains that enhance root development, stimulate immunity, or suppress harmful pathogens.
Technological advancements have also improved product stability and performance. Early microbial inoculants faced challenges such as short shelf life and sensitivity to environmental conditions. Today, improved formulation technologies such as liquid inoculants, encapsulation, and carrier-based systems have significantly increased product durability and ease of application. These innovations have contributed to broader commercial acceptance and global market expansion.
Key Market Trends
Several trends are shaping the growth of the Microbial Inoculants Market. One of the most significant trends is the expansion of organic farming, which relies heavily on bio-based inputs. Organic agricultural practices prioritize natural soil processes, making microbial inoculants an ideal fit. As consumer demand for organic foods rises, farmers are increasing their use of microbial products to maintain soil fertility and maximize yields without synthetic chemicals.
Another trend is the growing use of precision agriculture technologies. Farmers are now able to analyze soil conditions, nutrient levels, and microbial activity more accurately. This data helps determine which microbial inoculants are most suitable for specific crops and soil types, increasing adoption and improving outcomes. Microbial inoculants that support plant tolerance to stress conditions, such as extreme temperatures or salinity, are also gaining attention as climate change continues to influence growing conditions worldwide.
Sustainable agriculture initiatives promoted by governments, environmental organizations, and agricultural research institutions are expanding awareness of soil health. Soil quality is increasingly recognized as a key factor in long-term productivity, and microbial inoculants are widely used to restore biological activity in degraded soils. This trend is particularly strong in regions where intensive farming has diminished soil biodiversity.
Market Challenges
Despite their benefits, microbial inoculants face several challenges that limit widespread adoption. One of the primary challenges is the inconsistency of field performance. Microbial inoculants may behave differently depending on soil type, temperature, moisture levels, and farming practices. This variability can reduce farmer confidence and slow adoption in regions without strong extension services or technical support.
Product stability during storage and transportation is another challenge. Microorganisms are sensitive to environmental conditions such as heat, light, and humidity. Although modern formulations have improved stability, ensuring long shelf life remains essential for commercial success, especially in developing markets.
Regulatory hurdles also impact market growth. Many countries have strict regulations on microbial products, requiring detailed testing and registration processes. These procedures can be complex and time-consuming for manufacturers. Additionally, limited awareness among farmers—especially in rural areas—can restrict adoption, making education and demonstration programs crucial.
Market Scope
The Microbial Inoculants Market includes several product categories, each addressing different agricultural needs. Biofertilizers represent one of the largest segments, including nitrogen-fixing bacteria, phosphate-solubilizing microbes, and potassium-mobilizing organisms. These inoculants improve nutrient availability and reduce fertilizer costs for farmers. Biopesticides form another key segment, using fungi and bacteria to suppress soil-borne diseases and harmful insects. Plant growth–promoting inoculants enhance root development and nutrient uptake, contributing to higher crop yields.
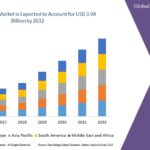
The market spans multiple regions. North America and Europe are leading adopters due to strong regulatory support for sustainable farming and high consumer demand for organic foods. These regions also benefit from advanced agricultural technologies and well-developed distribution networks. Asia-Pacific is experiencing rapid growth driven by large-scale agricultural activities, government promotion of biofertilizers, and rising awareness of soil degradation. Countries such as India and China are major contributors to market expansion. Latin America, particularly Brazil and Argentina, is adopting microbial inoculants to enhance soil health in extensive crop farming systems. The Middle East and Africa represent emerging markets where agricultural modernization is creating new opportunities.
End-user industries include agriculture, horticulture, greenhouse farming, turf management, and ornamental plant production. Agriculture remains the primary segment due to the widespread use of inoculants in cereal crops, vegetables, fruits, and oilseeds.
Market Size and Growth Drivers
The Microbial Inoculants Market is experiencing strong growth supported by rising adoption of sustainable farming practices. Increasing global concerns about soil degradation, pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions are driving governments and organizations to promote bio-based agricultural inputs. Rising food demand due to population growth further contributes to the need for high-yield, environmentally friendly crop production methods.
Technological advancements in microbial genomics, fermentation processes, and formulation science are improving product effectiveness and accessibility. Microbial inoculants can reduce dependency on chemical fertilizers, lower production costs, and enhance crop resilience, making them attractive for small-scale and commercial farms alike.
Investment in agricultural biotechnology, partnerships between research institutions and industry players, and expansion of distribution networks are expected to support a strong compound annual growth rate for the market in the coming years. Emerging regions with large agricultural bases present significant opportunities for manufacturers to expand their presence.
Conclusion
The Microbial Inoculants Market is positioned for significant global growth as agriculture shifts toward sustainability, soil health management, and environmentally friendly inputs. Microbial inoculants offer a natural way to enhance nutrient availability, strengthen plant growth, and improve soil biological activity. With advancements in biotechnology and rising awareness of sustainable farming, microbial inoculants will continue to play a central role in future agricultural practices. Stakeholders across the agricultural value chain—including farmers, manufacturers, researchers, and policymakers—stand to benefit from expanding opportunities in this evolving market.