The global energy landscape is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by an urgent need for sustainable and cost-effective heating solutions. In this shifting paradigm, wood pellet heating systems are emerging as a compelling alternative to traditional fossil fuels, carving out a substantial and growing market share. Fueled by environmental concerns, government incentives, and technological advancements, the Wood Pellet Heating System Market is poised for continued expansion, though it also faces unique challenges.
Market Size and Growth Projections:
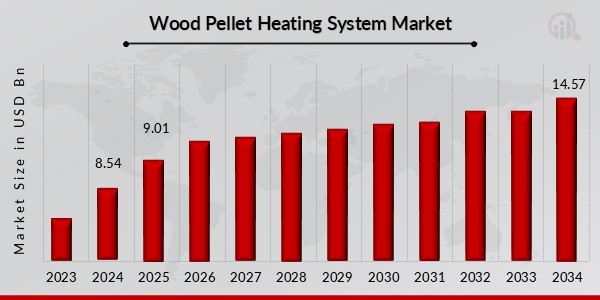
Wood Pellet Heating System Market Size was estimated at 8.54 (USD Billion) in 2024. The Wood Pellet Heating System Industry is expected to grow from 9.01 (USD Billion) in 2025 to 14.57 (USD Billion) by 2034. The Wood Pellet Heating System Market CAGR (growth rate) is expected to be around 5.48% during the forecast period (2025 – 2034).
Key Drivers Propelling Market Expansion:
Several factors are contributing to the increasing demand for wood pellet heating systems:
- Environmental Concerns and Decarbonization Goals: A primary driver is the escalating global focus on reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and achieving carbon neutrality. Wood pellets are considered a carbon-neutral fuel source because the CO2 released during combustion is largely offset by the CO2 absorbed by trees during their growth. This “closed-loop” carbon cycle makes them an attractive alternative to fossil fuels, which release stored carbon into the atmosphere. Governments and organizations are implementing stringent regulations and setting ambitious targets to curb emissions, further incentivizing the shift to renewable heating options.
- Government Policies and Incentives: Supportive government policies play a crucial role. Many nations offer incentives, grants, subsidies, and tax reductions to encourage the adoption of renewable energy sources, including biomass heating. Programs like the EU’s Renewable Energy Directive, the UK’s Renewable Heat Incentive (RHI), and similar initiatives in North America and Asia-Pacific are directly stimulating demand for wood pellet stoves and boilers.
- Rising Energy Costs and Economic Viability: Fluctuations and increases in the price of fossil fuels (oil, natural gas, and electricity) are prompting consumers and businesses to seek more stable and cost-effective heating solutions. Wood pellets often offer a competitive and predictable fuel cost, leading to long-term savings for users. Their high energy density ensures efficient burning, further contributing to their economic appeal.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in wood pellet heating system technology have significantly improved efficiency, convenience, and performance. Modern systems feature automated feeding, intelligent temperature control, self-cleaning mechanisms, and advanced combustion technologies. Condensing pellet boilers enhance energy conversion rates, while smart thermostats optimize heat distribution. These advancements make wood pellet heating a more practical and user-friendly option for diverse applications.
- Availability of Raw Materials: Wood pellets are primarily made from compressed sawdust and wood waste, byproducts of the timber and woodworking industries. This utilizes a readily available and often underutilized resource, promoting circular economy principles. Furthermore, sustainable forest management practices ensure a continuous supply of feedstock.
Regional Market Dynamics:
- Europe: Europe holds a dominant share in the global wood pellet market, driven by strong EU biomass policies, stringent environmental regulations, and efforts to meet emission targets. The region is both a major producer and consumer of wood pellets, with a growing number of pellet plants.
- North America: North America is experiencing increased wood pellet consumption due to price competitiveness with propane and heating oil, alongside the rapid replacement of older burners with more efficient systems.
- Asia-Pacific: The Asia-Pacific (APAC) region is projected to witness significant growth, fueled by favorable government policies promoting wood pellet use for power generation, increasing investments in renewable power, and a rising number of biomass power plants.
- South America and Middle East & Africa: These regions are also expected to see considerable growth, driven by investments in forestry and rising demand for residential cooking fuel and reduced reliance on coal, respectively.
Challenges and Future Outlook:
Despite the promising growth trajectory, the wood pellet heating system market faces certain challenges:
- Initial Investment Costs: The upfront cost of installing a wood pellet heating system can be higher than conventional fossil fuel systems, which can be a barrier for some consumers and businesses. However, the long-term fuel cost savings and potential government incentives often offset this initial outlay.
- Supply Chain Logistics: Managing the supply chain for wood pellets can be complex due to factors like transportation costs, storage requirements, and seasonal fluctuations in demand. Developing robust and efficient distribution networks is crucial for sustained market growth.
- Perception and Awareness: While awareness is growing, some regions still have limited understanding of the benefits and capabilities of modern wood pellet heating systems. Educational initiatives are necessary to address misconceptions and highlight their environmental and economic advantages.
- Competition from Other Renewables: The market faces competition from other renewable energy sources like solar and wind power, especially in the electricity generation sector. However, for heating applications, wood pellets offer a dispatchable and reliable solution that complements intermittent sources.
- Sustainability Concerns and Air Quality: While often touted as carbon-neutral, concerns regarding the true environmental impact of large-scale industrial wood pellet production, including forest sourcing practices and particulate matter emissions from combustion, have been raised. Continuous research and adherence to strict sustainability certifications are vital to address these concerns and maintain public trust.